Lyme in a nutshell
Lyme disease is an infectious disease causing a wide range of symptoms throughout all systems of the human body.
Ticks and other infections
Other infections (bacteria, viruses, parasites) can be transmitted by ticks. Although these can be transmitted independently, they are frequently transmitted concomitantly with Lyme disease, hence the term “co-infection.” These include bartonellosis, erlichiosis, babesiosis and pulmonary mycoplasmosis, to name but a few.
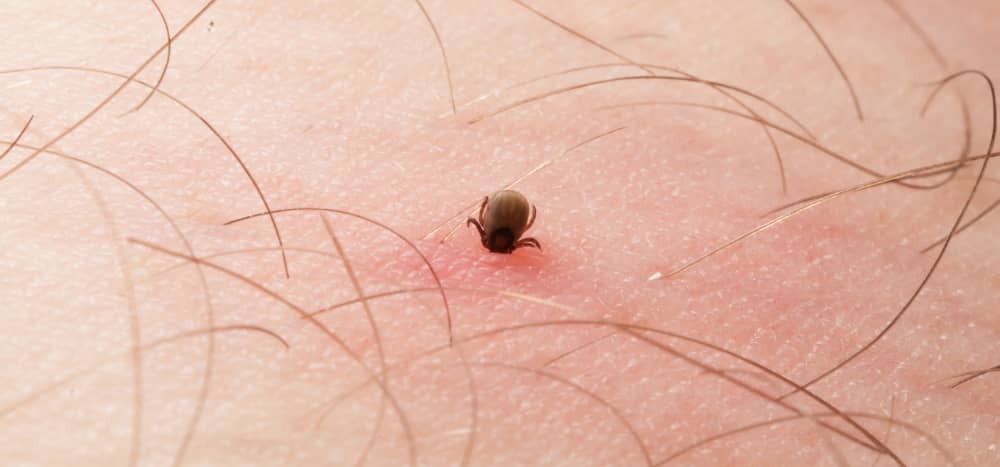
The Bite
Ticks feed on blood at every stage of their life: nymph, larva, adult. Although the bacterium (Borrelia) can be transmitted at all these stages, it is generally transmitted by those in the nymph stage. At this stage, the tick is so tiny (1 mm) that it goes unnoticed and is often compared to a poppy seed. In the adult stage, the tick measures approximately 2 mm to 2.5 mm and is similar to a sesame seed.
